pipe() Destination Driver
The pipe() driver sends messages to a named pipe like /dev/xconsole.
Important Information
Pipe is very similar to the file() driver, but there are a few differences, for example, pipe() opens its argument in read-write mode, therefore it is not recommended to use pipe() on anything else than real pipes. Pipes are created automatically so you don’t need to create the pipe using the mkfifo(1) command.
Status
| Architecture | Status |
|---|---|
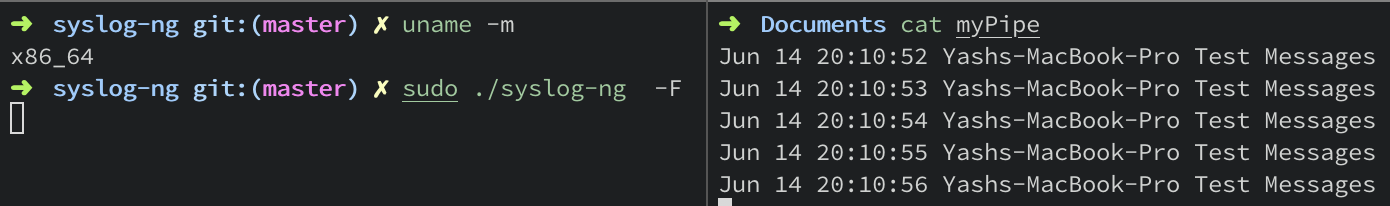
| x86 | Works |
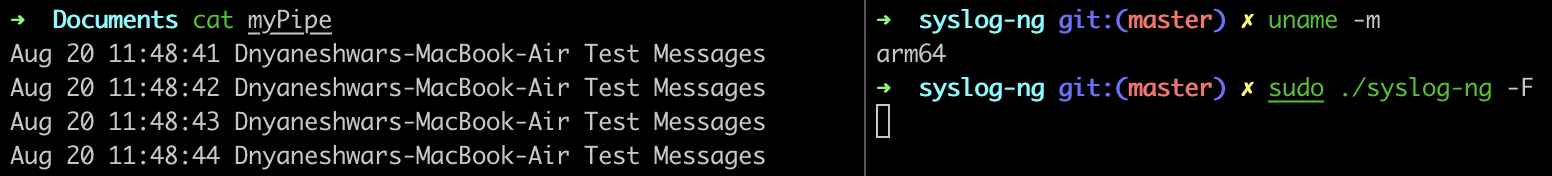
| ARM | Works |
How to Test
To test the pipe() destination driver, we create a pipe called “myPipe” and write data into it. And then we read data from this pipe.
Configuration File Used
@version: 3.31
@include "scl.conf"
source custom
{
example-msg-generator(
num(5)
template("Test Messages")
);
};
destination d_pipe {
pipe("/Users/yash/Documents/myPipe" perm(0755));
};
log {
source(custom);
destination(d_pipe);
};
Proof