unix-dgram() Source/Destination Driver
The unix-dgram() source driver open an AF_UNIX socket and start listening on it for messages. Whereas unix-dgram() destination driver send messages to a UNIX domain socket.
Important Information
Unix-dgram() is used on BSDs and uses SOCK_DGRAM semantics: this may result in lost local messages if the system is overloaded.
In the official documentation, /dev/log is the default entry for system logging. This, in fact, is a socket, not a regular file or a pipe. MacOS, however, uses /var/run/syslog for the same. This needs to be kept in mind while referring to the documentation.
Status
| x86 | Works |
|---|---|
| ARM | Works |
How to Test
To test the unix-dgram() drivers, we will run two instances of syslog-ng. One where we are transmitting data to a socket using the unix-dgram() destination driver that needs to be tested. And another that will listen for the data on the socket using the unix-stream() source driver.
Source Configuration File
@version: 3.31
@include "scl.conf"
options {
stats-freq(10);
time-reopen(10);
};
source s_dgram {
unix-dgram("/var/run/syslog");
};
destination console{
file(/dev/stdout);
};
log {
source(s_dgram);
destination(console);
};
Note: We need to run the source driver first as it will open the socket to which the destination driver connects to.
Destination Configuration File
@version: 3.31
@include "scl.conf"
options {
stats-freq(10);
time-reopen(10);
};
source custom {
example-msg-generator(
num(20)
freq(5)
template("Message to Default Socket")
);
};
destination d_dgram {
unix-dgram("/var/run/syslog");
};
log {
source(custom);
destination(d_dgram);
};
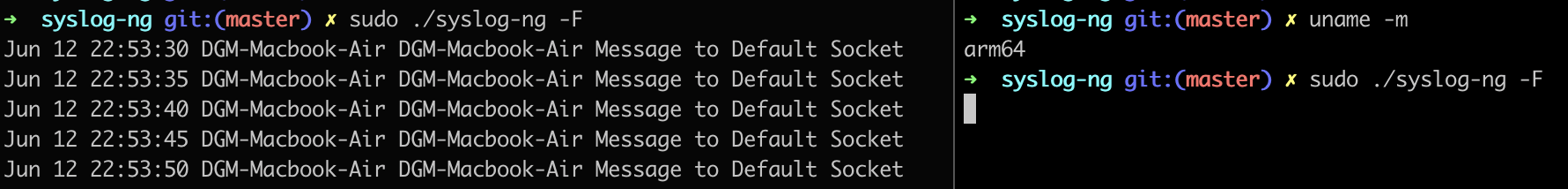
Proof